



MOMMA PROBIOTICS Probiotics For Every Stage of Motherhood
Promotes a healthy vaginal microbiome for conception and pregnancy with prebiotics and probiotics plus, digestion, immunity and healthy blood glucose levels.*
- Probiotics formulated for moms and moms-to-be
- Helps promote healthy blood glucose levels
- Advanced blend of 18 strains and 14 billion CFUs in acid-resistant capsules
- Super clean ingredients, no artificial fillers, or binders
-
90-Day, 100% Money Back Guarantee
-
24/7 Customer Support
-
Easy Returns
Frequently Bought Together
Key Ingredients
Potent Ingredients & Nothing Else
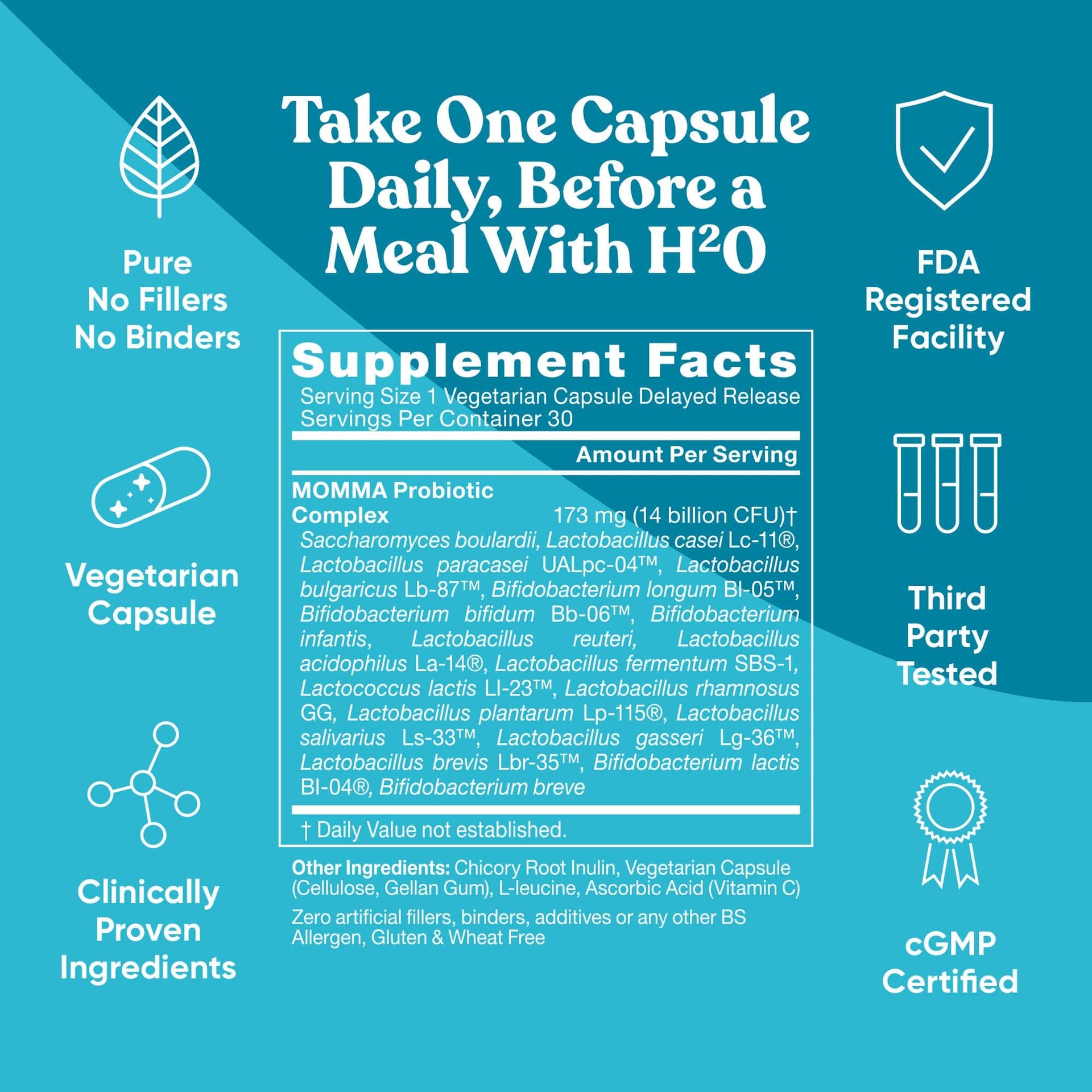
Momma Probiotic Complex
Advanced blend of 18 strains and 14 billion CFUs uniquely designed to protect the balance of beneficial bacteria for your digestive system and vaginal microbiome for both Mom and Baby’s health during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Product Information
MOMMA PROBIOTICS contain an advanced blend of 18 strains and 14 billion CFUs uniquely designed to protect the balance of beneficial bacteria for your digestive system and vaginal microbiome. This probiotic blend helps support comfortable digestion, regularity, and natural immunity plus vaginal health support. The advanced capsule is designed to withstand stomach acids and release probiotics directly into the lower gut where they can be most useful.
Probiotics Formulated For Moms
Advanced blend of 18 strains and 14 billion CFUs to help support digestive comfort, regularity, immune support, vaginal health and healthy glucose levels.
Digestive & Vaginal Health Support When You Need It Most
This specifically designed blend supports the vaginal microbiome for vaginal health support when you are TTC, pregnant and postnatal.
Helps Promote Healthy Blood Glucose Levels
During pregnancy to support mom
Acid-Resistant Capsules
Powerful stomach acids can destroy most probiotics before they arrive in your lower gut. MOMMA PROBIOTICS capsules are made to withstand digestive acids, ensuring that 14 billion probiotic CFUs (colony forming units) arrive in your lower gut.
Everything you need, nothing you don’t
Our capsules are vegetarian, free from artificial colors, fillers, binders, additives, gluten & animal testing; 3rd party tested for purity & potency with a cGMP-certified blend
Just 1 Capsule A Day
For 24/7 support & protection take 1 easy-to-swallow vegetarian capsules daily with a meal and water to deliver maximum daily support
The following studies back up MOMMA ingredients for supporting Mom and Baby’s health during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Lactobacillus acidophilus La-14, Lactobacillus plantarum Lp-115, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, Lactobacillus paracasei Lpc-37, Lactobacillus reuteri IE1, Bifidobacterium lactis Bl-04, Bifidobacterium longum Bl-05, Bifidobacterium bifidum BB-06, Lactococcus lactis Ll-23, Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM-I-1079, Lactobacillus casei Lc-11, Lactobacillus salivariusLs-33, Lactobacillus gasseri Lg-36, Lactobacillus bulgaricus Lb-87, Lactobacillus fermentum SBS-1, Lactobacillus brevis Lbr-35, Bifidobacterium breve Bb-03, Bifidobacterium infantis Bi-26, Inulin Fructooligosaccharide (FOS) Prebiotic
Improving Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Pregnant Women:
Patients were randomized into two groups, with one group taking a placebo, and the other taking a probiotic which contained Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus casei and Bifidobacterium bifidum.
The researchers found, “Overall, probiotic supplementation among women with GDM for six weeks had beneficial effects on FPG, serum hs-CRP, plasma TAC, MDA and oxidative stress index” for pregnant women.
Preventing Atopic Dermatitis and Eczema:
The effects of selected probiotic strains on the development of eczema (the PandA study)
Researchers tested Bifidobacterium bifidum, Bifidobacterium lactis, and Lactococcus lactis against a placebo in a randomized, double-blind study. They found, “This particular combination of probiotic bacteria shows a preventive effect on the incidence of eczema in high‐risk children, which seems to be sustained during the first 2 years of life. In addition to previous studies, the preventive effect appears to be established within the first 3 months of life.”
“Prevention regimen with specific probiotics administered to the pregnant and breast-feeding mother, that is, prenatally and postnatally, is safe and effective in reducing the risk of eczema in infants with allergic mothers positive for skin prick test.”
In this double-blind study, 415 pregnant women were randomized into two groups. One took placebo milk, the other probiotic milk. The probiotic formula contained Lactobacillus rhamnosos GG, L. acidophilus La-5 and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis Bb-12.
Six years after the children were born, the researchers checked back with them to see if the probiotics had helped prevent allergy-related diseases. They found, “Maternal probiotic ingestion alone may be sufficient for long term reduction in the cumulative incidence of [atopic dermatitis] AD, but not other allergy related diseases.”
Treating Vaginal and Rectal Infections and Preventing Pre-Term Birth:
Ingestion of Probiotics: Optional Treatment of Bacterial Vaginosis in Pregnancy
L. acidophilus in particular may help to fight bacterial vaginosis in pregnant women. Also, “Although scientific confirmation is still needed, probiotics may be especially important for reducing the preterm birth rate in pregnant women. It has been claimed that intrauterine infection with BV may antedate the pregnancy [38]. Probiotics can safely be used before pregnancy or in the first trimester. Moreover, it may be used as an adjunctive to therapy in the second trimester, avoiding potential side effects and teratogenicity of standard treatments. Probiotics may well be the answer.”
This small study found that the use of prenatal probiotics reduced rectal and vaginal colonization by B Streptococcus.
Glucose and Insulin Control:
“The present study demonstrated that improved blood glucose control can be achieved by dietary counselling with probiotics even in a normoglycaemic population and thus may provide potential novel means for the prophylactic and therapeutic management of glucose disorders.”
“Daily consumption of probiotic yogurt for 9 weeks maintains serum insulin levels and might help pregnant women prevent developing insulin resistance.”
This study on 256 pregnant women tested Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and Bifidobacterium lactis Bb12 against a placebo. The researchers found that the probiotics helped decrease the risk of gestational diabetus mellitus.
“There are indications for a protective role in preeclampsia, gestational diabetes mellitus, vaginal infections, maternal and infant weight gain and allergic diseases.”
For Brain Development:
Probiotic, Prebiotic, and Brain Development
According to this paper, there are “strong indications” that the gut microbiota has an effect on the gut-brain axis. As such, it might be possible for probiotics and probiotics to impact brain development.
How many bottles should I order?
In order to get the full benefits, we recommend purchasing and saving more with our discounted three bottle or wellness subscription packages. This will ensure you have enough supply on hand to achieve your goals, while taking advantage of the best pricing and free shipping. Use code EUNATL10 for 10% off 2 bottles, EUNATL15 for 15% off 3 bottles, or EUNATL20 for 20% off 4 or more bottles.
How do I use it?
Take one (1) capsule, daily with food and 8 ounce glass of water. Take before and during pregnancy.
What quality standards are in place?
All our products are bottled in the United States of America under strict federal guidelines to ensure quality. Fillers, binders, and other artificial additives are never used in our manufacturing process. Facilities are FDA registered and inspected to cGMP standards, exceeding FDA 21 CFR Part 111 regulations.
How long will it take to see results?
Individual results vary; however, customers have reported results within a few days of starting the supplement.
Is it safe to order online from your website?
Yes. We incorporate physical, electronic, and administrative procedures to safeguard the confidentiality of your personal information, including Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) for the encryption of all financial transactions through the website.
How long does shipping take?
Most orders are processed within 1 business day. Standard US shipping is 3 to 4 business days via USPS First Class, expedited is 2 business days via USPS Priority Mail, and international shipping is 7 to 14 days. Tracking number will be immediately provided once shipped.
Can I take it with other products?
MOMMA is a natural dietary supplement formulated to be combined with a healthy diet and lifestyle. Consult with your health care practitioner before using this supplement with other products.
What if this product does not work for me?
We offer a full refund on the purchase price of our supplement formulas any time within 90 days (up to 3 bottles full or empty) for orders shipped in the United States. To process a refund, please email us for instructions on returning your bottles. Once your return is received, a credit will automatically be applied to your original method of payment.
Before using Momma Probiotics, I was super gassy and bloated all the time. Almost anything I ate was making me feel super uncomfortable afterwards to the extent that I didn't look forward to eating anything. After about a week of use, I noticed a significant decrease in my digestive issues. Not only does my gut feel better, but urination seems to have improved also (steady stream with complete emptying). I'm glad to have found this product and highly recommend it.
This has helped me and all of my levels have improved with this pregnancy compared to my last.
Great
1,000% recommend. It contains like every different probiotic strain known to man, and it definitely won't disappoint. I loved taking it so much that I ended up giving my toddler 1/2 a capsule every day because he went through a stage of having chronic diarrhea, and lo and behold, he had perfect bowl movements within a week.Get it.
I specifically bought these probiotics as I read that it might help as I had tested positive for Group B Strep when I was only 12 weeks pregnant. I had been taking these probiotics since then. Additionally I would occasionally drink some probiotic water and yogurts. Well I am here to proudly say at 36 weeks pregnant I was retested and am now GBS negative. Clearly I’m no medical professional, but I give all the credit to these vitamins. They are a little pricey but worth it for me.
I used to have problems digesting peanut butter, milk and other stuff, also constipation and bloating. I helped me a lot. Its pricey indeed...
Amazing love this vitamins , would be into buying again ! recommended 100% after postpartum
Praised be! (in my hand maids voice.)I bought this directly from the site but my prenatal came thru website.Jesus knows I'm 41 with 3 kids having another one was not expected. Sick af. Literally! Nauseated! Bloated! And beyond constipated. After taking this i realized how bad I was constipated due to the 3 day deadly flatulence. But upon the first day of taking the pill all nausea was gone. By the third day pushing it all out and no more deadly gas. every morning, at the same time, regular. No more constipation. And again no nausea.Again, in my handmaid voice, May the Lord open many doors for you. Thanks.
Great product, easy to take, and overall a pleasant experience.
These vitamins are easy to take and make me feel great. I especially like the vitality ones for hair health and growth. I can see a difference before one bottle was finished. I'll continue to take these for sure 👍
You May Also Like















