





PRENATAL GLOW — The Ultimate Clean & Complete Prenatal
Promotes baby’s healthy development plus supports mom’s energy, glucose and stomach sensitivity with a clean and comprehensive prenatal. High-potency prenatal formulated with premium nutrients, such as I-methyfolate and vegan DHA to support a healthy and comfortable pregnancy.*
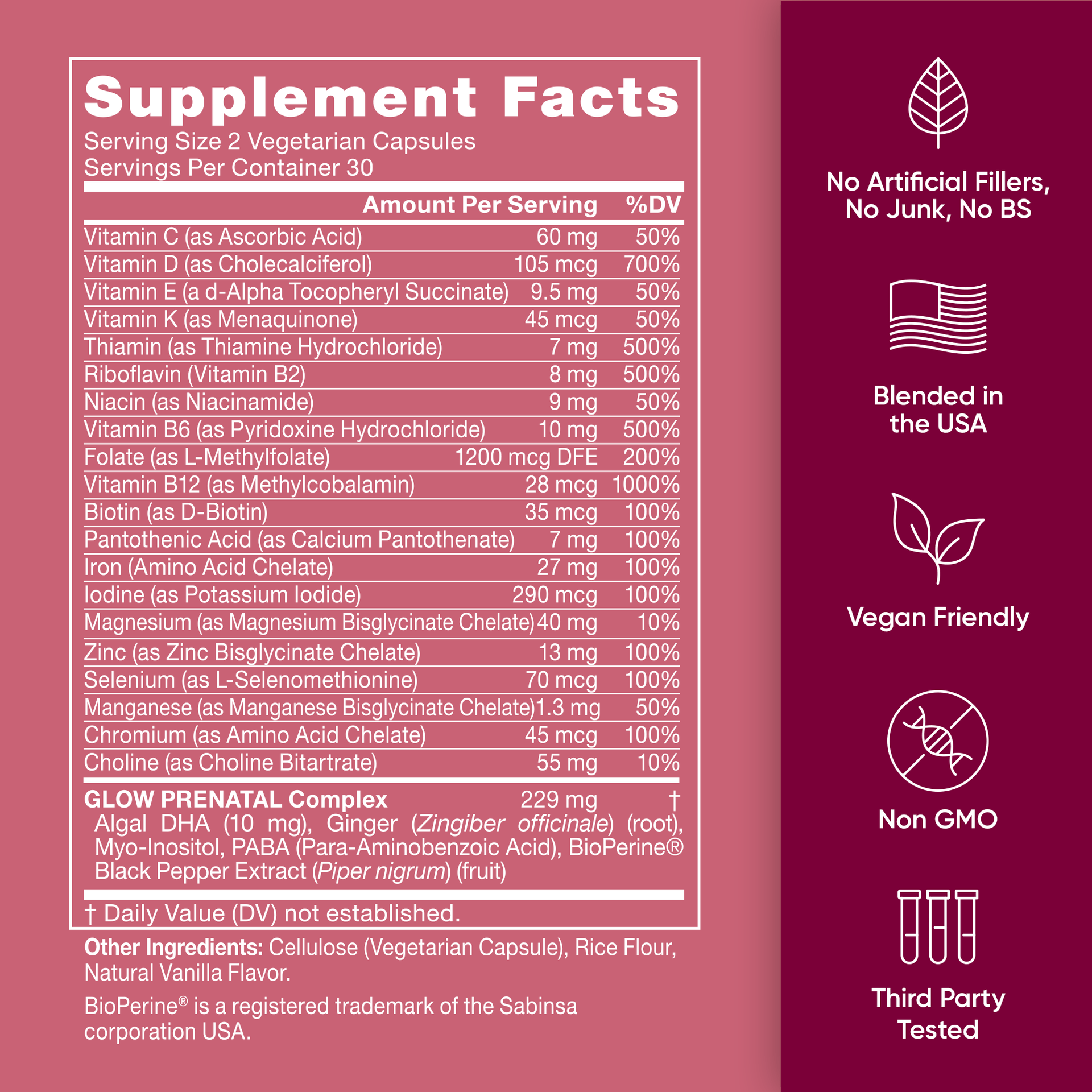
- Vegan pre & post natal care formulated with 25 premium vitamins and minerals
- Made with doctor-preferred form of folate for the most bioavailable form
- Created for mom & baby to grow and have a comfortable pregnancy
- Super clean ingredients, no artificial fillers, or binders
-
90-Day, 100% Money Back Guarantee
-
24/7 Customer Support
-
Easy Returns
Frequently Bought Together
Key Ingredients
Potent Ingredients & Nothing Else

L-Methylfolate
Folate is a mission-critical nutrient when pregnant, for both the developing fetus and for maternal health. For example, folate is essential to aid in the development of the fetus' nervous system support healthy neural tube and birth development. Our prenatal features the preferred, body-ready, highly-bioavailable form of folate known as L-Methylfolate.

AquaCelle® Algal DHA
DHA is a marine-based, healthy omega-3 fat, which is referred to as an essential fatty acid because your body needs it but cannot produce it on its own, so it must get it from dietary sources. This is important during pregnancy where DHA has well-established benefits for the fetus as well as the health of the pregnant mother, such as improved birth outcomes, cognitive and visual development, maternal mood, heart health, and more.

Ginger Extract
Ginger is a rare botanical in the sense that it has both a long history of use and safety during pregnancy, when it is frequently used, with varying degrees of success, to provide support for pregnancy-related nausea, vomiting, morning sickness, motion sickness, and indigestion.

Myo-Inositol
Myo-Inositol -- a naturally occurring sugar commonly found in cereals, corn, legumes, and meat that supports proper insulin function and healthy insulin sensitivity -- isn't just for fertility. Indeed, myo-inositol can also safely and effectively be taken during pregnancy to support the metabolic health of the pregnant mother and fetus, as well as supporting full-term pregnancy.

BioPerine® Nutrient Enhancer
BioPerine® s a clinically tested black pepper extract that has been shown to enhance the absorption of a range of nutrients – including certain micronutrients, like vitamin B6 and selenium – to help ensure more of the valuable nutrition gets delivered where you need it most.
Product Information
PRENATAL GLOW is a clean and comprehensive pre and postnatal formulated with 20+ vitamins and minerals both mom and baby need to grow and have a comfortable pregnancy. Easy to take and formulated with algal DHA and choline to support brain and eye development for baby.
Created For Mom & Baby
unlike most prenatal that focus only on baby, PRENATAL GLOW is formulated for sensitive stomachs with ginger and vanilla for a more pleasant experience, even during your 1st trimester, and supports glucose sensitivity
From The Makers Of CONCEPTION FOR HER:
The leading fertility brand on Amazon, who knows conception health, is the “more-in-one prenatal” clean and complete, vegan pre & postnatal care.
Scientifically Backed Support
Premium prenatal vitamin with 25 lab-tested, vital nutrients; these vitamins and minerals enhanced to be more bioavailable support optimal development for baby
Made With Doctor Preferred Form Of Folate
Not all folate is the same, we included the most bioavailable form of folate at clinically validated dose.
Promotes Healthy Glucose Levels
in a healthy normal range for mom.
Targeted Vegan Prenatal Complex:
prenatal vitamins with DHA and folic acid paired with super ingredients TRAACS chelated minerals, and myo-inositol; made for sensitive stomach with ginger and vanilla for a more pleasant pregnancy, even during your 1st trimester and made with vegan algal based DHA
Absorb All Our Goodness:
Our supplements are made with super clean ingredients in a cGMP-certified facility – formulated for bioavailability to improve nutrient absorption so you get the most out of each serving. Free of artificial fillers, binders, artificial fillers, gluten, wheat, and dairy
Just 2 Capsules A Day
for support & protection: Usage directions, take 2 easy-to-swallow vegetarian capsules daily with a meal and water to deliver maximum daily support
The following studies back up GLOW ingredients for supporting the nutritional needs of Mom and Baby during pregnancy. Doing so can prevent deficiencies for both Mom and Baby before and after birth, and may help prevent adverse outcomes.
AquaCelle® Algal DHA
DHA supplementation and pregnancy outcomes
This research found that supplementing with 600 mg of DHA daily during the second half of gestation could help to reduce premature births and increase birth weights.
DHA supplementation: Current implications in pregnancy and childhood
This review notes, “Adequate DHA availability in the fetus/infant optimizes brain and retinal maturation in part by influencing neurotransmitter pathways." Based on the research conducted, the authors of the study suggest that DHA can indeed have neurological benefits for infants, but that further research is needed to establish best practices for composition and dosing.
Ginger
Ginger for nausea and vomiting in pregnancy:: Randomized, double-masked, placebo-controlled trial
Pregnant women participating in this study who took ginger experienced fewer vomiting episodes than those who took a placebo. Taking the ginger also reduced nausea compared to the placebo. The dosage was 1 g of ginger per day.
Ginger syrup as an antiemetic in early pregnancy
This research also found one gram of ginger daily to be useful in combating nausea and vomiting during the first trimester.
Myo-Inositol
According to this study, supplementing with myo-inositol may help to reduce the likelihood of gestational diabetes mellitus.
“MDFM [myo-inositol, Dchiro-inositol, folic acid and manganese] administration after 30 days in pregnancy improved glycemic and lipidic parameters, with significant gain after 60 days, without affecting diastolic blood pressure levels.
PABA
PABA Study Shows 75% Success Rate with Getting Pregnant
“A 1942 study parked interest and reported that 16 women who had fertility problems took 100mg of PABA 4x a day for 3-7 months. 75% became pregnant. The effects of PABA on fertility has not been studied since.”
Vitamin C
Vitamin C supplementation in pregnancy
“Women supplemented with vitamin C alone or in combination with other supplements compared with placebo or no control were at decreased risk of having a placental abruption.”
Vitamin D
Vitamin D supplementation for women during pregnancy
“Supplementing pregnant women with vitamin D in a single or continued dose increases serum 25‐hydroxyvitamin D at term and may reduce the risk of pre‐eclampsia, low birthweight and preterm birth. “
The researchers note that many women are deficient in vitamin D during pregnancy, and that supplementing with vitamin D, particularly during winter, could reduce the chances of osteoporotic fracture in children. It is noteworthy that this study ran nine years, so it did not just look at infant development, but at child development through that age.
Vitamin D effects on pregnancy and the placenta
This paper provides a useful overview of how the placenta and vitamin D work together to drive immune system response.
Vitamin E
Low Maternal Vitamin E Intake during Pregnancy Is Associated with Asthma in 5-Year-Old Children
As the title of this study indicates, pregnant women who get less vitamin E may be compromising the respiratory health of their offspring, who are more likely to develop asthma.
This animal study provides support for treatment with vitamin C and vitamin E. It may reduce rates of tissue damage and fetal malformation.
Vitamin K
A review of vitamin K, epilepsy and pregnancy
This research says that mothers who are epileptic should consider supplementing with vitamin K during the months leading up to delivery as well as during labor.
B Vitamins
Vitamin B12 Metabolism and Status during Pregnancy, Lactation and Infancy
Deficiency in vitamin B12 during pregnancy is common, especially among vegetarians, and even among omnivores who simply don't eat a lot of meat. This can result in an infant born with deficient levels of B12. The researchers emphasize that vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to permanent neurological damage. Thus, it is very important to make sure that vitamin B12 levels remain sufficient during pregnancy and breast-feeding.
Vitamin B1 status in pregnancy
Out of 599 pregnant women participating in this study, “25–30% were found to be thiamin-depleted in respect of erythrocyte transketolase saturation in comparison with a group of over 300 male and female blood donors. This proportion remained constant throughout gestation. As a consequence, vitamin B1 supplementation is recommended to prevent subclinical metabolic disturbances of thiamin-dependent enzyme systems.”
Disturbance of vitamin B6 metabolism in pregnancy
“On the basis of these experiments it is suggested that pregnant women be given a daily dose of vitamin B6, equivalent to 10 mg. of pyridoxine hydrochloride, in order to correct the biochemically demonstrable vitamin B6 deficiency.”
Riboflavin status in pregnancy
In a study on 651 pregnant women, “25% of the pregnant women in the first trimester-increasing to 40% at term-were shown to be significantly riboflavin-depleted in comparison to a group of over 300 male and female blood donors.
“Adding riboflavin tends to enhance the effect of iron‐folate supplementation.”
Marginal biotin deficiency during normal pregnancy
In this study, researchers found that during the first trimester, it is common for marginal biotin deficiency to happen.
Pantothenic acid status of pregnant and lactating women.
Pregnant and lactating women have lower levels of pantothenic acid than those who are not pregnant or lactating. The researchers suggest an increase in consumption of pantothenate may be valuable.
Folate
“MDFM [myo-inositol, Dchiro-inositol, folic acid and manganese] administration after 30 days in pregnancy improved glycemic and lipidic parameters, with significant gain after 60 days, without affecting diastolic blood pressure levels.”
Accelerated folate breakdown in pregnancy
Researchers in this study report that the catabolism of folate is increased during pregnancy, which is why pregnant women require around 200-300 μg of folate supplementation daily to maintain optimum levels.
Dietary and serum folate: their influence on the outcome of pregnancy
“Women with a low mean daily folate intake (</-240 microgram/d) had an approximately twofold greater risk of preterm delivery and infant low birth weight after maternal characteristics, energy intake, and other correlated nutrients were controlled for. Lower concentrations of serum folate at week 28 were also associated with a greater risk of preterm delivery and low birth weight.”
Iron
In a study of 150 for pregnant women, it was found that iron stores declined rapidly during the first trimester. While supplementation failed to prevent this, it did manage to prevent deficiency later during the course of pregnancy.
Anemia and iron deficiency: effects on pregnancy outcome
According to this paper, when pregnant mothers are deficient in iron, it is possible for infants to likewise become iron deficient and develop anemia. The researchers suggest that pregnant women supplement with iron.
Pregnancy and Iron Deficiency: Unresolved Issues
“Maternal iron deficiency anemia may be associated with adverse outcomes, including preterm delivery and higher maternal mortality.”
Daily oral iron supplementation during pregnancy
This study found that supplementing with iron while pregnant can reduce the chances of developing iron deficiency or anemia.
Iodine
Sufficient levels of iodine are essential during pregnancy in order to prevent “repercussions” for both the mother and the developing fetus.
The importance of iodine nutrition during pregnancy
This research suggests that iodine be administered to pregnant women, but that iodized salt is not the optimum delivery system. “In European countries, presently it is proposed that iodine is given to pregnant women and breast-feeding mothers by systematically administering multivitamin tablets containing iodine in order to reach the recommended dietary allowance of 250 μg iodine day-1.”
The Effects of Iodine Deficiency in Pregnancy and Infancy
Neurological cretinism may result from insufficient iodine.
Magnesium
Magnesium supplementation in pregnancy. A double‐blind study
“Magnesium supplementation during pregnancy was associated with significantly fewer maternal hospitalizations, a reduction in preterm delivery, and less frequent referral of the newborn to the neonatal intensive care unit. The results suggest that magnesium supplementation during pregnancy has a significant influence on fetal and maternal morbidity both before and after delivery.”
The effect of oral magnesium substitution on pregnancy-induced leg cramps
This study noted particular benefits for reducing leg cramps during pregnancy by supplementing with oral magnesium.
Zinc
Changes in plasma and hair concentrations of zinc, copper, chromium, and manganese during pregnancy
Zinc levels drop during early pregnancy, and decline further in late pregnancy.
While inconclusive, this study did find that supplementing with zinc may help to reduce dysfunctional labor pattern incidences.
Determinants of maternal zinc status during pregnancy
“Zinc deficiency in pregnant experimental animals limits fetal growth and, if severe, causes teratogenic anomalies. Although the data from human studies are not consistent, similar outcomes have been observed and were associated with poor maternal zinc status … Supplemental zinc may be prudent for women with poor gastrointestinal function or with any of these conditions during pregnancy.”
Selenium
The researchers suggest that a “small increase” in selenium might help to stave off preeclampsia.
The role of selenium in human conception and pregnancy
When selenium levels are low early during a pregnancy, a low birth weight might result. Miscarriages, gestational complications, and immune and nervous system damage in fetuses also are associated with deficient selenium levels.
Managnese
“MDFM [myo-inositol, Dchiro-inositol, folic acid and manganese] administration after 30 days in pregnancy improved glycemic and lipidic parameters, with significant gain after 60 days, without affecting diastolic blood pressure levels.”
Whole blood manganese levels in pregnancy and the neonate
The researchers who conducted the study believe that manganese may play a "vital role in fetal development."
Chromium
The effect of parity on maternal hair chromium concentration and the changes during pregnancy.
“If adequate amounts of chromium are not taken during pregnancy, deficiency may result with increasing parity.”
Choline
“In summary, choline supplementation of the diet among women in their third trimester of pregnancy, at a level exceeding the current AI, improved infant processing speed relative to maternal consumption of the AI. This finding suggests that the current AI level for choline during pregnancy may need to be increased for improved offspring cognitive functioning.”
These researchers did well placing their study within context of other human and animal research into this topic, so this article is also worth reading for the bigger picture.
How many bottles should I order?
In order to get the full benefits, we recommend purchasing and saving more with our discounted three bottle or wellness subscription packages. This will ensure you have enough supply on hand to achieve your goals, while taking advantage of the best pricing and free shipping. Use code EUNATL10 for 10% off 2 bottles, EUNATL15 for 15% off 3 bottles, or EUNATL20 for 20% off 4 or more bottles.
How do I use it?
Take one (1) capsule twice daily with food and an 8 ounce glass of water. Take before, during, and after pregnancy. Capsules may be opened and put into a smoothie or juice.
What quality standards are in place?
All our products are bottled in the United States of America under strict federal guidelines to ensure quality. Fillers, binders, and other artificial additives are never used in our manufacturing process. Facilities are FDA registered and inspected to cGMP standards, exceeding FDA 21 CFR Part 111 regulations.
How long will it take to see results?
Individual results vary; however, we recommend to use the product before, during, and after pregnancy.
Is it safe to order online from your website?
Yes. We incorporate physical, electronic, and administrative procedures to safeguard the confidentiality of your personal information, including Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) for the encryption of all financial transactions through the website.
How long does shipping take?
Can I take it with other products?
GLOW is a natural dietary supplement formulated to be combined with a healthy diet and lifestyle. Consult with your health care practitioner before using this supplement with other products.
What if this product does not work for me?
We offer a full refund on the purchase price of our supplement formulas any time within 90 days (up to 3 bottles full or empty) for orders shipped in the United States. To process a refund, please email us for instructions on returning your bottles. Once your return is received, a credit will automatically be applied to your original method of payment.
Glow prenatal vitamins have been my go to vitamins for years now. Ever since I found out I have the MTHFR gene I’ve taken these vitamins. I absolutely love them!
It came faster than I thought, thank you
A little pricey but it’s worth it. Been using it before & after pregnancy. All good ingredients, but need to have calcium included.
So, I’m in my first trimester and honestly I don’t take them like I should because of morning sickness. But if their prenatal is anything like their other products, I’m sure they’re amazing!
I am grateful for a good clean prenatal and specifically has the folate our bodies need and handle better than the synthetic folic acid!
Love this prenatal!
My Favorite prenatals, the best! 👌
Came on time! I don’t buy from any other brand
I’ve noticed a big change in my complexion and overall feeling after taking these prenatals over the ones you can just buy in stores. They don’t make me nauseated like my old ones did & I feel better knowing they are a quality company that makes quality products!
Love these prenatals! They have everything my baby and I need!
You May Also Like
















